From the Campfire to the Stovetop: A History of the Dutch Oven
If you're looking for a History of the Dutch Oven, look no further! This blog post delves deep into the origins and features of this iconic cooking pot. Whether you're an experienced chef or just starting out in the kitchen, you'll find everything you need to know about Dutch ovens right here.
A Dutch oven is a thick-walled cooking pot with a tight-fitting lid. Dutch ovens are versatile, durable pots that can be used for slow-cooking, baking, and braising. They are usually made of cast iron or ceramic, although some models are made of aluminum or other materials. The term "Dutch oven" can be used to refer to either the pot itself or the type of food cooked in it.
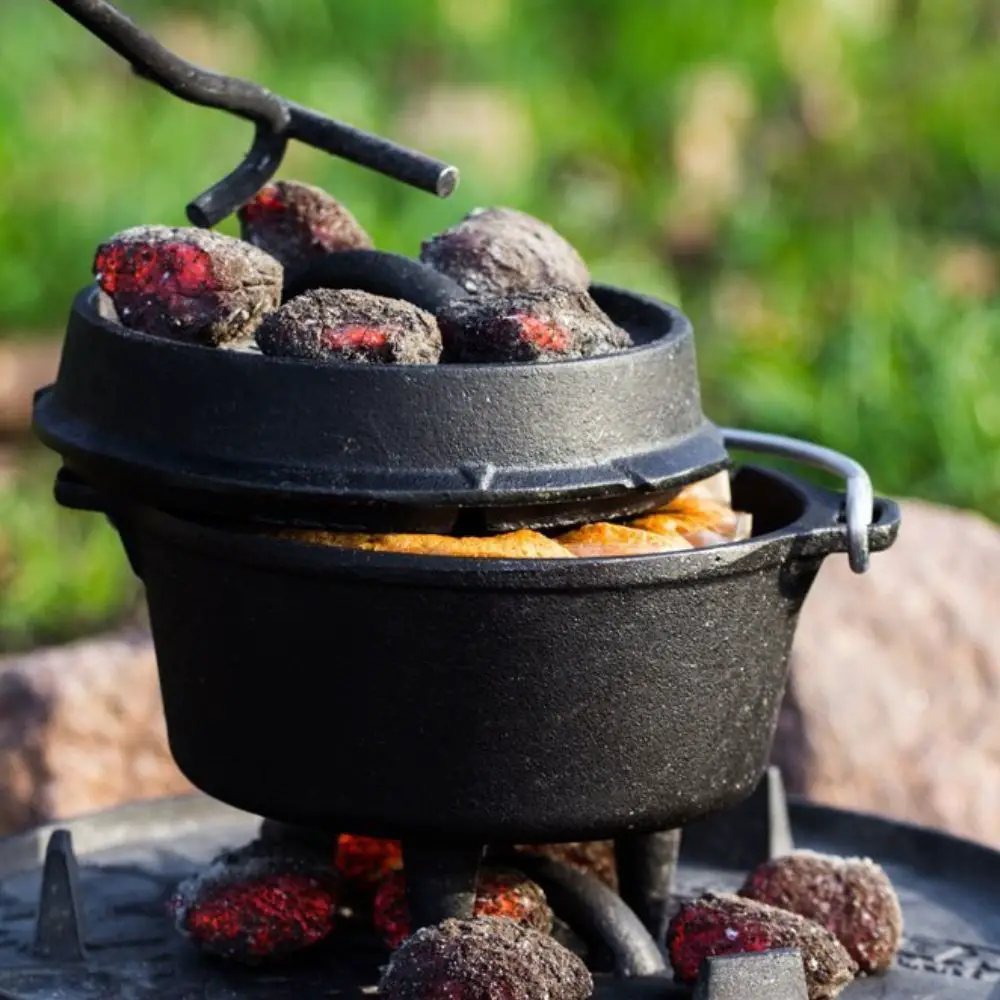
Dutch ovens have been used for centuries to cook all sorts of food, from stews and roasts to bread and desserts. Nowadays, Dutch ovens are most commonly used for camping and outdoor cooking. They can be placed directly on top of a campfire, which makes them perfect for cooking stew, soup, or anything else that needs to be slow-cooked.
However, Dutch ovens are not just for camping they can also be used indoors on the stovetop or in the oven. No matter how you choose to use them, Dutch ovens are a versatile and convenient way to cook all sorts of delicious food.
A Brief History
The Dutch oven is thought to have originated in the Netherlands in the 1600s. These early versions of the Dutch oven were made from brass and had legs so that they could be suspended over a fire. They were also often fitted with a tight-fitting lid to prevent ash and embers from getting inside the pot.
However, during the same time, similar cookware was popular in England, they were called “cauldron pots.” These cauldron pots were brought to the Netherlands by English immigrants in the 1600s. Brass was the preferred material for cookware during those days in Europe and the Dutch could prepare Brassware in the most efficient way to give a smoother finish.
The cauldron pots were then modified by the Dutch to be more suitable for cooking over an open fire. The bottom of the pot was flattened and the legs were lengthened so that it could be placed directly on hot coals.
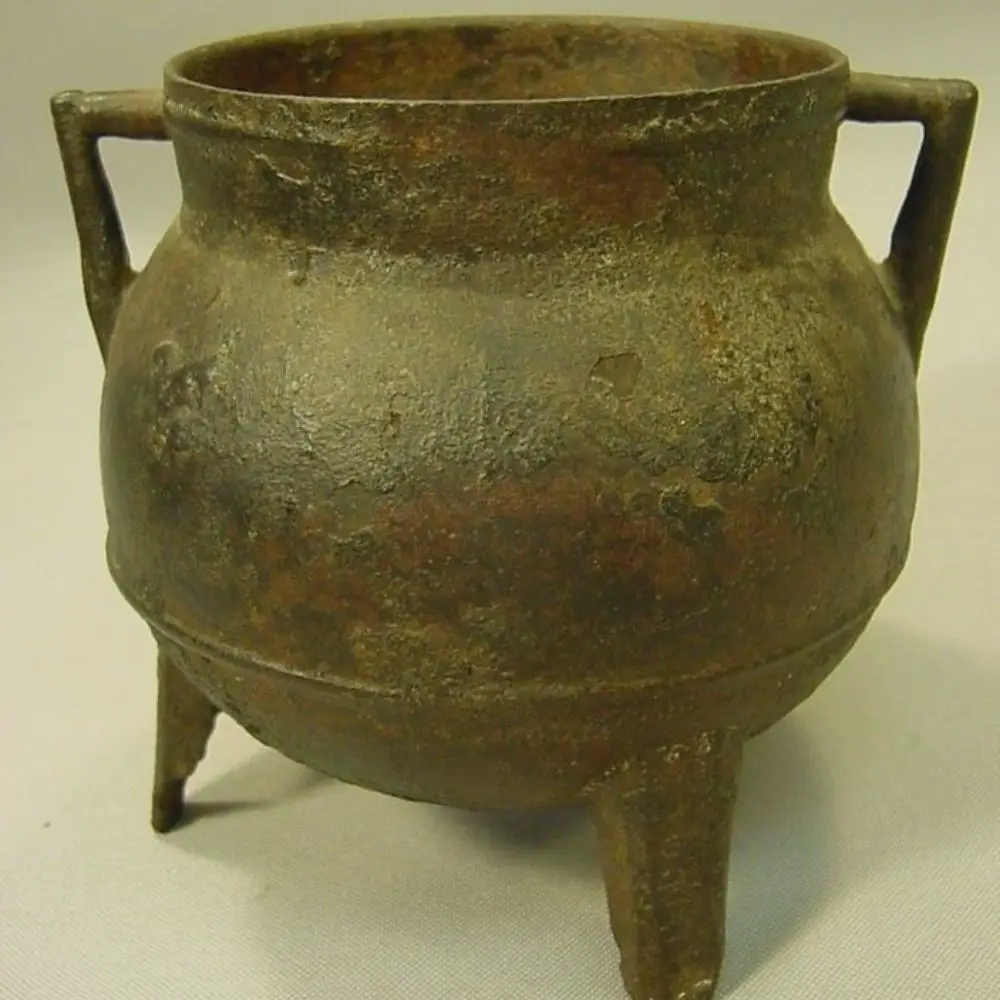

Then the English inventor Abraham Darby tried to maximize profit but replacing brass with Cast Iron and patenting a new technique of preparing cast iron in a cost-effective manner. This cast Dutch oven iron soon became a staple in households all across Europe.
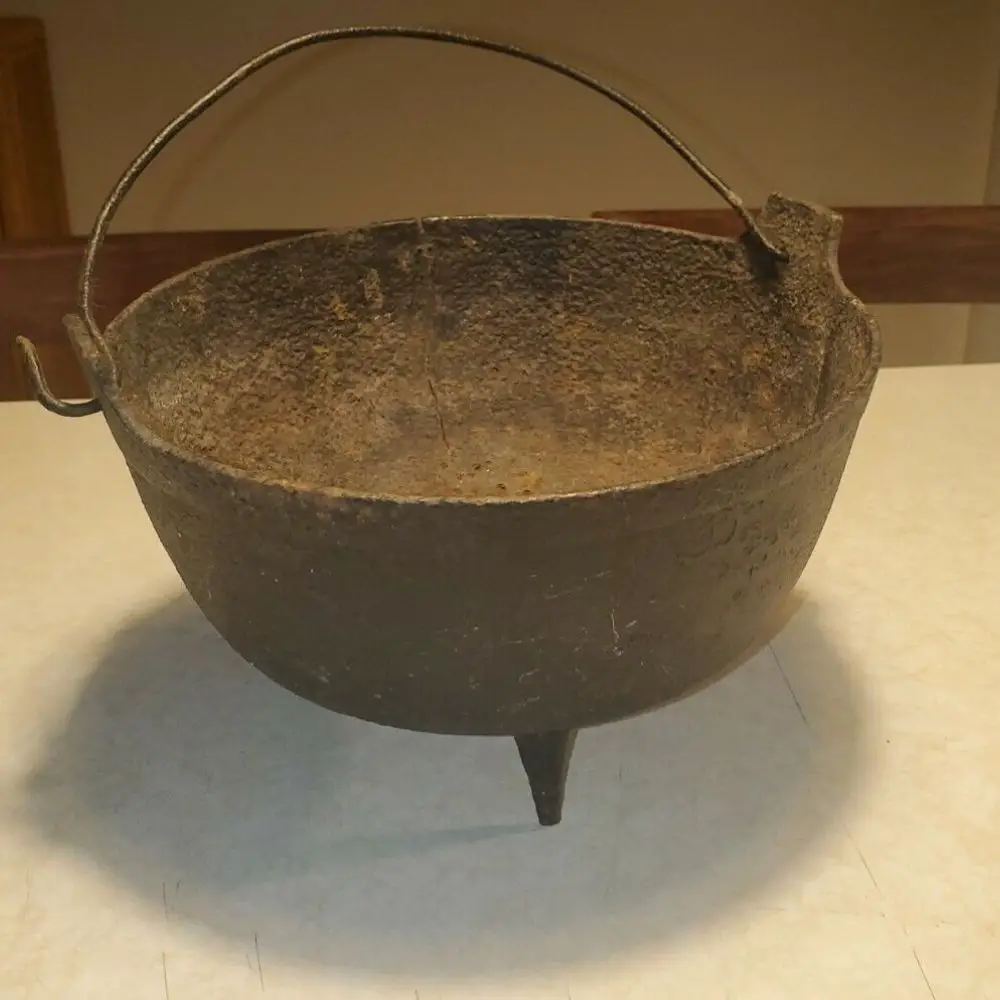

Eventually, it made its way to America, where it was adopted by settlers and Native Americans alike. Because these early pots were so heavy, they were often used as doorstops or banks! It wasn't until the 1800s that homemakers began using Dutch ovens for cooking.
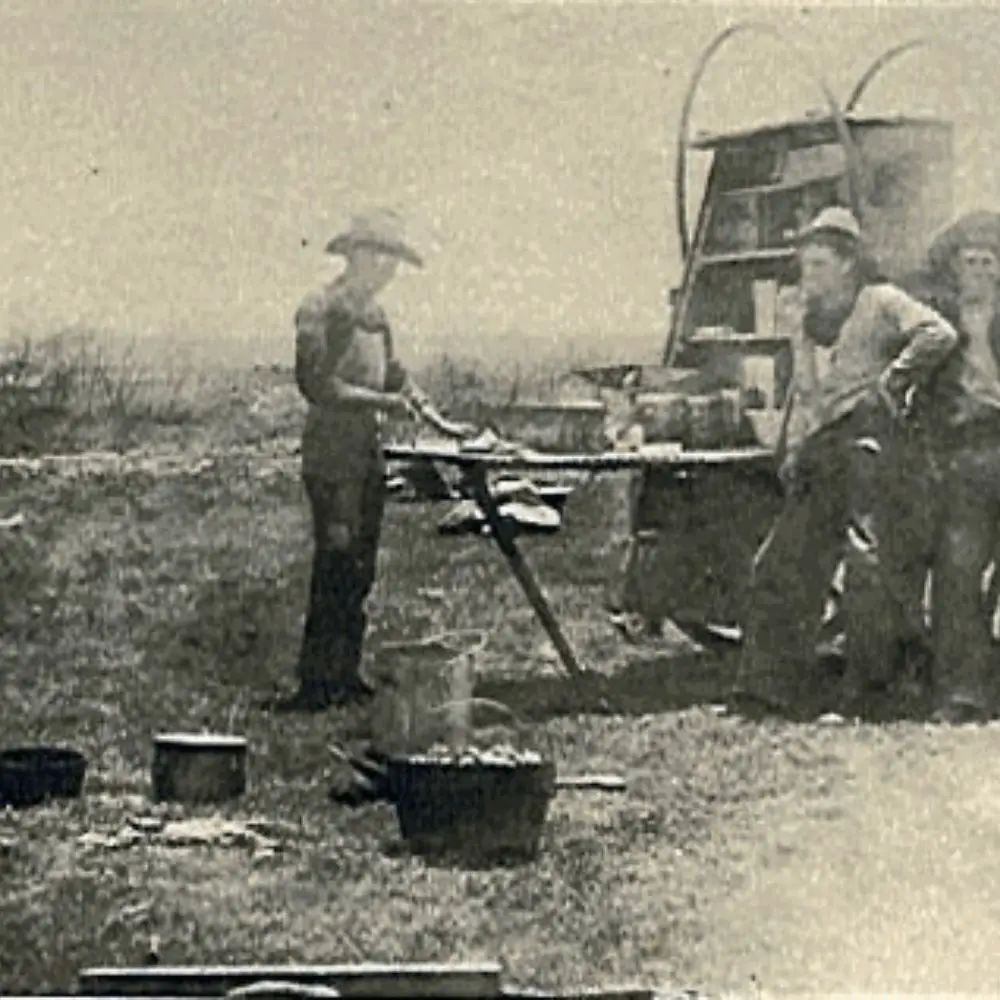

Since then, they have become popular worldwide and can be found in almost all the countries of the world. Each of them varies slightly in shape and size and is known by different names like Bedourie Oven in Australia, Potjie in Africa, Coquille in France, Tetseunabe in Japan, and Chugunok in Russia among others.
Different Types of Dutch Ovens
Depending on their structure, there are two main types of Dutch ovens: those with legs and those without.
Legless Dutch ovens are similar to (and sometimes mistakenly called) "casserole dishes" or "braisers", though they are quite different from each other. These types of pots can be placed directly on top of a heat source, which makes them ideal for slow-cooking meats and stews. Legless Dutch ovens often have deep sides, which help prevent spills when cooking over an open flame.
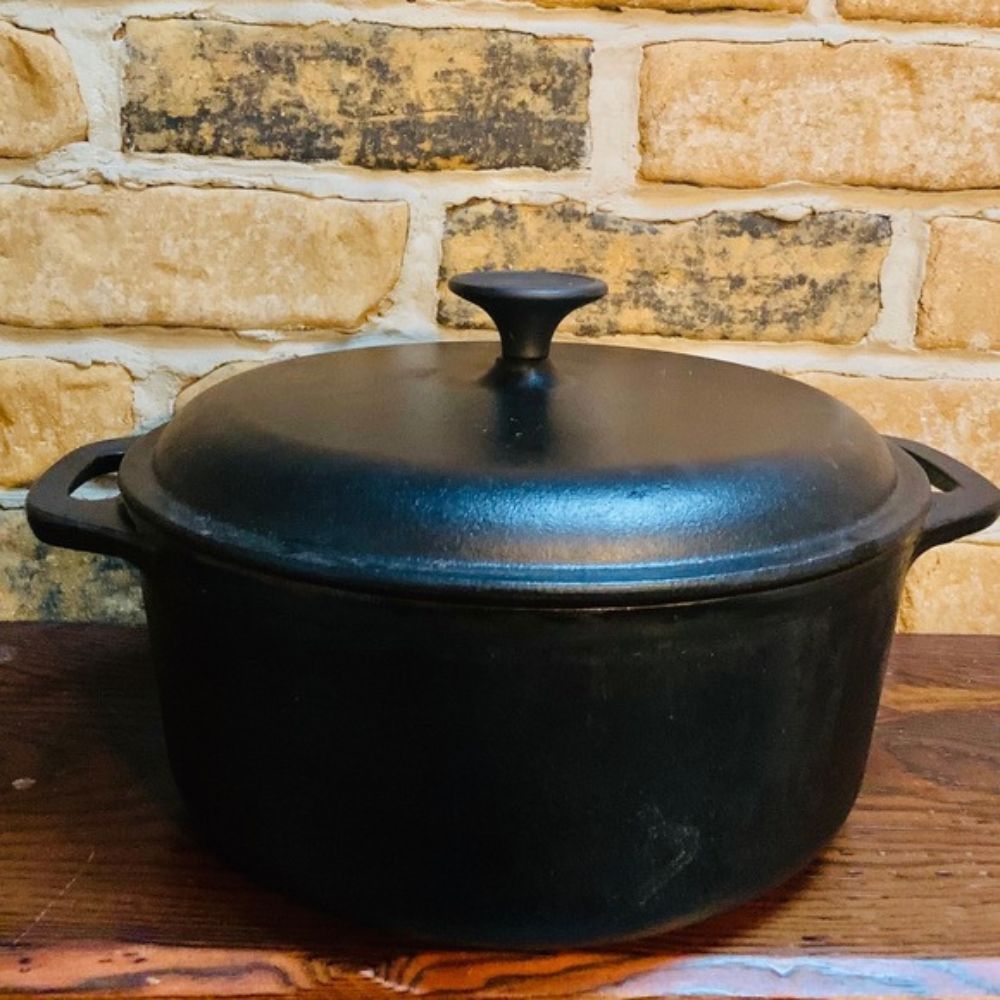

Dutch ovens with legs are sometimes called "chuck boxes." These pots usually have shallower sides than legless models, making them better suited for baking bread or roasting meat. Some models come with a second set of handles that make it easier to carry them when they're full.
If you're planning on doing a lot of cooking over an open fire, a legless Dutch oven is probably your best bet. However, if you're mostly going to be using your pot indoors, either type will work fine.

In addition to these two main types, there are also many different materials that Dutch ovens can be made from. The most common material is cast iron, which has excellent heat retention properties and can withstand high temperatures without warping. Ceramic Dutch ovens are also becoming increasingly popular because they don't require as much maintenance as cast iron pots do.
Aluminum Dutch ovens are lightweight and inexpensive but they don't retain heat as well as other materials do. Stainless Steel and even titanium Dutch ovens are also available but they are much more expensive than other types.
No matter what material you choose, make sure that your Dutch oven is oven-safe and has a tight-fitting lid. These two features are essential for any good Dutch oven.
You can further have enameled or non-enameled ovens. Enameled Dutch ovens are coated with a layer of enamel, which prevents rusting and makes them easier to clean. These are used for indoor cooking. While for cooking on open fire Non-Enameled Dutch Ovens are better suited that lack the enamel layer.
Experience brighter and better skin with Kojic Acid Soaps even when you are roughing it out in the outdoors.
Conclusion
The next time you use your Dutch oven, take a moment to think about its rich history. From its humble beginnings in the Netherlands to its current status as a kitchen staple, the Dutch oven has come a long way.
Today, it remains just as popular as ever thanks to its versatility, durability, and ability to produce perfectly baked bread and pastries. Whether you're cooking for yourself or for a group of friends, your Dutch oven will help you create mouth-watering dishes that are sure to please everyone at the table. And who knows? With its enduring popularity and versatility, it may just be around for another 400 years!
If you want to bake the perfect bread and want a proper dutch oven, you can find the best Dutch Oven for baking bread here. But if you want a camping Dutch oven for your next trip, check out our article and find the best available options.

Also, check out some of our other articles: