When 'Sport' Goes Too Far: Why Are Hunting Regulations Passed
Many people view hunting as a barbaric sport that should be banned altogether. However, there are many reasons why hunting is actually a vital part of ecosystem management. Check out our short blog post and know why were hunting laws passed.
Many hunters are familiar with the term "fair chase" and understand that it encompasses the ethical, sportsmanlike pursuit of game animals. What some hunters may not realize, however, is that fair chase is a relatively new concept in the history of hunting.
For most of human history, hunting was a subsistence activity undertaken only to put food on the table. Hunting wasn't until the 19th century that it began to be seen as a leisure activity pursued for its own sake.
As more and more people began to hunt for sport, concerns began to arise about the impact this would have on wildlife populations. In response to these concerns, state and federal governments began enacting hunting regulations designed to limit the take of game animals and protect wildlife populations from over-exploitation.
Today, hunting regulations are an important tool for conservationists and wildlife managers who use them to ensure that game populations remain healthy and sustainable into the future. But why were hunting laws passed? Let's take a closer look.

| What are Hunting Regulations? | Purpose of Hunting Regulations | Enforcement of Hunting Regulations |
|---|---|---|
| Rules and guidelines set by authorities to control the practice of hunting. | To conserve wildlife, maintain ecological balance, ensure ethical hunting practices, and safety considerations. | Implemented by local, state, or national wildlife agencies and enforced by game wardens or similar authorities. |
Animals That Were Hunted to Extinction
Hunting regulations were initially enacted in response to the over-exploitation of certain wildlife species. Before these laws, many species were hunted to the point of extinction; some of the most recent ones include:
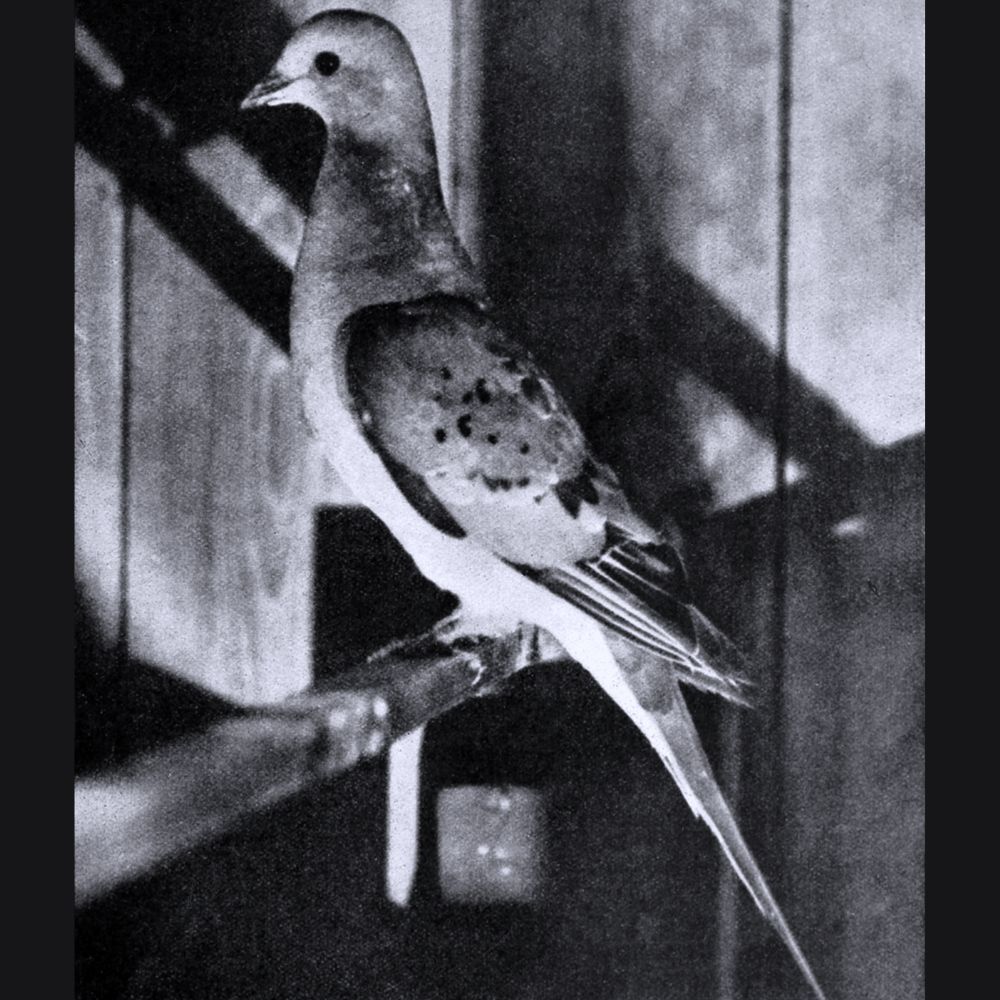
i. Passenger Pigeon: Once one of North America's most abundant bird species, passenger pigeons were hunted relentlessly for food until they went extinct in 1914.

ii. Great Auk: The great auk was a flightless bird found in North America and Europe that was hunted for its meat, eggs, feathers, and oil until it went extinct in 1844.
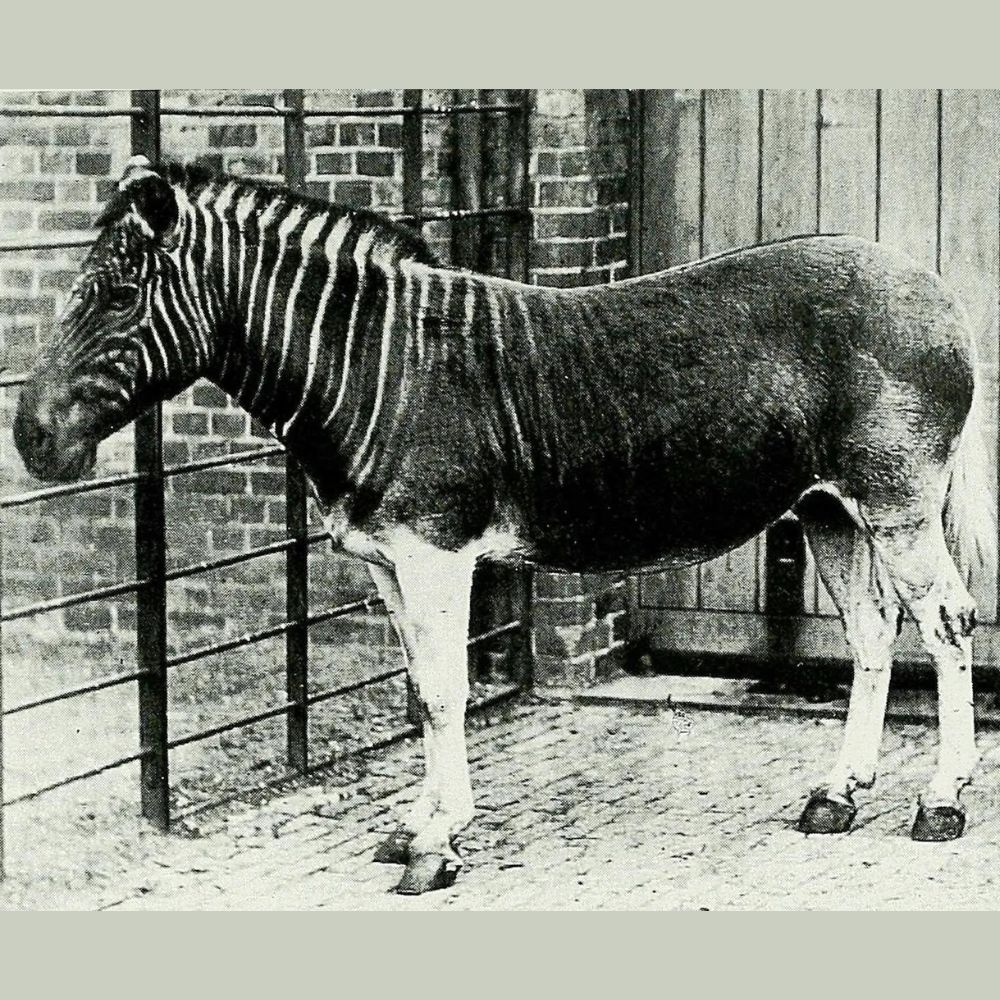
iii. Quagga: The quagga was a subspecies of zebra found in South Africa that was hunted because it competed with the forage of domestic animals until it went extinct in 1883.

iv. Tasmanian Tiger: Also known as the Thylacine, this marsupial carnivore native to Australia was hunted by farmers who believed it preyed on their livestock until it went extinct in 1936.
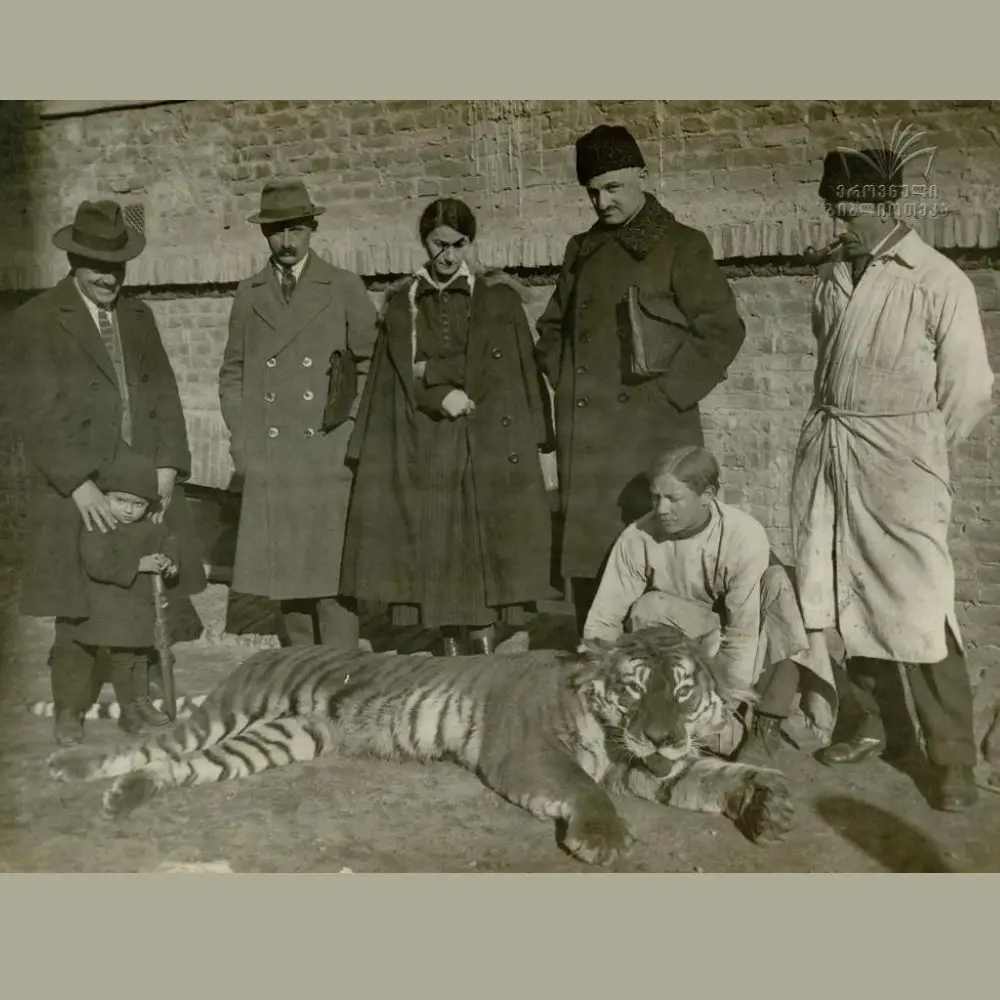

v. Caspian Tiger: This large subspecies of tiger found throughout Central Asia and the Middle East was hunted illegally as trophies and for its fur until it went extinct around the 1960s. However, there were some unconfirmed sightings as late as the 1970s.

vi. Caribbean Monk Seal: Found only in warm waters around Florida and Caribbean islands, humans heavily hunted this seal species for its oil until it went extinct around 1952.

vii. Heath Hen: This grouse-like bird once inhabited grasslands along the East Coast, but habitat loss combined with overhunting led to its extinction around 1932.
| Wildlife Conservation Aspect | Role of Hunting Regulations |
|---|---|
| Population control | Regulate the number of certain species to prevent overpopulation or extinction. |
| Habitat conservation | Protect habitats from destruction caused by unregulated hunting. |
| Species conservation | Help maintain healthy populations of hunted species. |
History of Hunting Laws
These unregulated hunts decimated entire populations of animals and left them vulnerable to extinction. In response, governments began passing laws to control and limit the take of game animals to protect and preserve wildlife populations. However, some of the initial laws were drawn to support hunting, and some even announced bounties for hunts.
One of the first recorded hunting laws in the United States was passed in 1627 by the Massachusetts Bay Colony, making fowling and fishing free for citizens with a few restrictions. In an effort to better regulate and protect wildlife in their area, in 1646, Portsmouth passed a law setting up deer hunting season with financial penalties enforced on anyone who broke it.
In 1900, Congress passed the Lacey Act, which made transporting illegally harvested wildlife across state lines illegal. This act also gave federal authorities jurisdiction over wildlife crimes.
The Migratory Bird Treaty Act was passed in 1918, which protected migratory birds from being hunted or killed without a permit.
The Endangered Species Act was signed into law in 1973, which provided protection for endangered species and their habitats due to rapid expansion and development.
Today, numerous federal and state laws regulate hunting practices to ensure the sustainable use of wildlife resources.
| Legislative Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Law Creation | Laws are created by government bodies at various levels (local, state, national) based on the need for wildlife conservation. |
| Law Enforcement | Laws are enforced by designated authorities such as game wardens or wildlife officers. |
Why Were Hunting Laws Passed?
Hunting regulations are important for several reasons.
1. Ensure healthy and sustainable game populations
By limiting the number of animals that can be harvested each year, hunting regulations prevent the over-exploitation of wildlife populations and allow animals time to reproduce and replenish their numbers. Hunting laws prevent overhunting and preserve animal populations in the future.
2. Maintain balance in ecosystems
Hunting regulation controls predator-prey relationships, thereby maintaining a healthy ecological balance. For example, by allowing only a certain number of deer to be harvested each year, deer populations are kept in check, and predators like wolves and coyotes don't have an easy meal every time they go hunting.
This maintains a healthy balance between predators and prey and helps prevent one species from becoming too dominant or too scarce in an ecosystem. In short, hunters play an important role in conserving wildlife.
3. Promote fair chase
Hunting laws are passed to ensure that all hunters have an equal opportunity to harvest game animals. By limiting the number of tags or permits available for each species, hunting regulations help prevent wealthy hunters from purchasing all of the best tags and leaving nothing but scraps for everyone else. This ensures everyone has a fair chance at harvesting a trophy animal or filling their freezer with venison for the winter.
4. To ensure the safety of both hunters and non-hunters alike
Another important reason for hunting regulations is to ensure the safety of everyone involved. When hunters follow the rules, it minimizes the chances of accidents happening. In addition, it also helps to protect non-hunters who may be in the vicinity.
5. To uphold ethical standards
Finally, hunting regulations help to uphold ethical standards within the hunting community. These standards ensure that animals are not being cruelly treated and give hunters a sense of responsibility for their actions.
| Ecological Aspect | Impact of Hunting |
|---|---|
| Predator-Prey Balance | Can help maintain balance. |
| Biodiversity | Overhunting can decrease biodiversity. |
| Ecosystem Health | Revenue from hunting licenses can contribute but can also lead to overpopulation. |
See how Joe Rogan explains hunting to Russel Brand in this video:
Different Types of Hunting Regulations
As hunting became more widespread and commercialized, it also became clear that regulations were necessary to ensure the sustainability of wildlife populations and prevent overhunting.
Today, hunting laws exist in many countries worldwide, including the United States. These laws vary depending on the country or region. However, the four main factors covered by hunting regulations are :
Bag Limits
Bag limits refer to the number of animals that can be legally hunted during a specific period. The purpose of bag limits is to prevent overhunting and ensure that wildlife populations remain healthy.
Wildlife management agencies set these limits based on scientific data about population size and growth rates. Species typically set bag limits and may vary depending on factors such as the location of the hunt, population size, habitat quality, and hunting pressure.
For example, in Massachusetts, hunters can take two antlered deer annually with at least one antler three inches or longer. Antlerless deer (any deer without antlers or antlers less than three inches) may also be taken during certain seasons.
Season Dates
Season dates refer to the period during which hunting is allowed for a specific species. Wildlife management agencies also set these dates based on scientific data about breeding cycles and migration patterns. Season dates ensure that hunting occurs only when it will have minimal impact on wildlife populations and won't exceed the area's carrying capacity.
Season dates can vary depending on the species being hunted and the location of the hunt. For example, in Montana, elk hunting season typically runs from late August through early December. But this will again vary from one district to another.
Tag Quotas
Tag quotas refer to limits on the number of tags (licenses) issued for a particular species during a specific period. Wildlife management agencies set these quotas based on scientific data about population size and growth rates. The purpose of tag quotas is to prevent overhunting and ensure that wildlife populations remain healthy.
Tag quotas can vary depending on the species being hunted and other factors such as location or method of take (e.g., archery vs. rifle). For example, in Arizona's 2022-23 Hunting Regulations Publication, specific tag quotas are listed for each type of big game animal available for harvest.
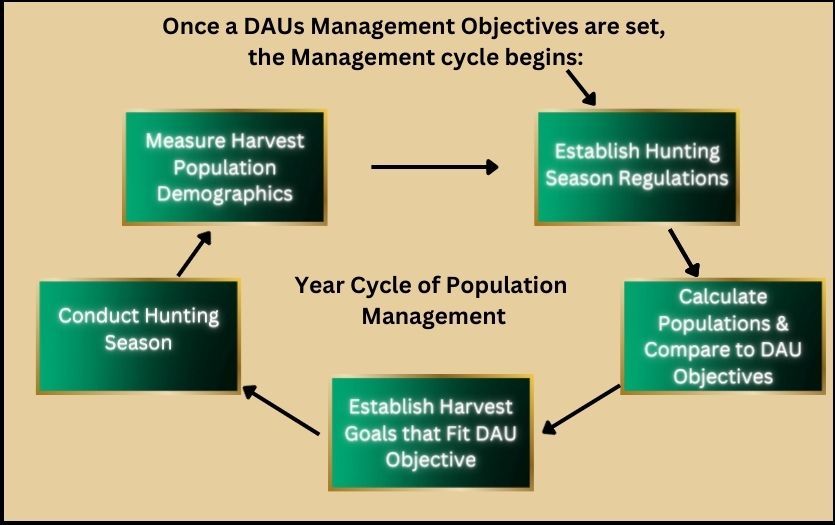
However, determining a precise quota for game animals is not easy. With areal counting of the animals being the only recourse to receive a fractional number of animal populations in any given region.
This data is compared with past numbers and potential projections to discern patterns in herd migrations by individual species' Data Analysis Units (DAUs). These data are further utilized by the Game Management Unit (GMU) to develop restrictions set every year.
Maximize your hunting safety! Learn how to attach a haul line to your firearm the right way!
Other Factors
Weapon Restrictions
Weapon restrictions refer to limitations on the types of weapons that can be used for hunting. These restrictions are often implemented to promote safety or fairness in hunting practices. For example, some states may prohibit hunters from using high-powered rifles for certain games because they pose a greater risk of injury or death.
Weapon restrictions can also vary depending on the location of the hunt and other factors. For example, in Texas, hunters have restrictions on using shotguns with buckshot or slugs for deer hunting but not rifles.
Licensing Requirements
Licensing requirements refer to the process by which hunters obtain legal permission. This may involve passing a hunter education course or obtaining a license from a government agency.
Other Restrictions
Restrictions may also be in place, such as prohibitions on baiting, the use of drones or other devices, the number of dogs that can be used for blood trailing, taking of certain species at night, and the practice of spotlighting, etc. These are all put in place to ensure that hunting is done responsibly and with respect for wildlife populations and habitats.
By understanding bag limits, season dates, tag quotas, weapon restrictions, and licensing requirements
| Ethic | Description |
|---|---|
| Fair chase | The game should have a reasonable chance to evade the hunter. |
| Respect for life | Hunters should aim for a quick and humane kill. |
| Utilization | Hunters should make full use of the animal. |
Overview of How Hunting Regulations Vary Across Different Regions
Hunting regulations vary widely across different regions due to differences in wildlife populations, habitat quality, cultural attitudes toward hunting, and other factors. For example:
- In North America, bag limits are often set based on population estimates and scientific data.
- In Europe, many countries have strict weapon restrictions and require hunters to pass rigorous tests before obtaining a license.
- In Africa, many countries have implemented conservation programs that allow for sustainable trophy hunting while protecting endangered species.
Overall, it is important for hunters to understand and abide by local hunting regulations in order to ensure the sustainability of wildlife populations and promote safe and ethical hunting practices.
Final Words
Hunting regulations play an important role in conservation efforts by helping to ensure that game populations remain healthy and sustainable into the future.
In addition, they help maintain balance in ecosystems and promote fair chase by ensuring that all hunters have an equal opportunity to harvest game animals.
So next time you grumble about getting a permit or filling out paperwork before going hunting, remember that these regulations are in place for good reason!
And if you are a hunter, check our section on hunting gear to find the best hunting gear you can buy.
Why Are Hunting Regulations Passed
Hunting regulations are passed and implemented by local, state, or national wildlife agencies and enforced by game wardens or similar authorities. They serve the following purposes:
| Purpose | Description |
|---|---|
| Conservation of Wildlife | Hunting regulations help to control the population of certain species to prevent overpopulation or extinction. |
| Maintenance of Ecological Balance | Regulated hunting helps to maintain the predator-prey relationship and ensure that ecosystems remain healthy. |
| Ethical Hunting Practices | Hunting regulations ensure that hunting is conducted in a fair and humane way, with respect for the animals being hunted. |
| Safety Considerations | Hunting regulations enforce safety measures, such as firearm safety and legal compliance, to protect hunters and the public. |
Also, check out some of our other quick reads: